Git与Github使用
1. Git概述
Git这种分布式版本控制工具,客户端提取的不是最新版本的文件快照,而是把代码仓库完整地镜像下来(本地库)。这样任何一处协同工作用的文件发生故障,事后都可以用其他客户端的本地仓库进行恢复。因为每个客户端的每一次文件提取操作,实际上都是一次对整个文件仓库的完整备份。
2. 常用命令
- 设置用户签名
git config --global user.name 用户名 - 设置用户签名
git config --global user.email 邮箱
注意:这里设置用户签名和将来登陆Github的账号没有任何关系。
- 初始化本地库
git init - 查看本地库状态
git status - 将工作区的文件添加到暂存区
git add 文件名 - 将暂存区的文件提交到本地库
git commit -m "日志信息" 文件名
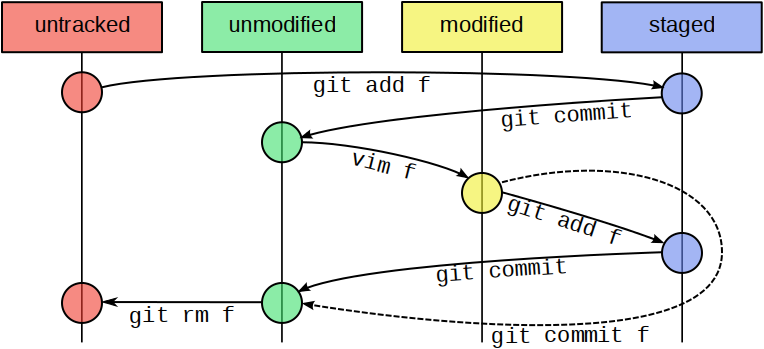
- 查看版本信息(HEAD经过的历史记录)
git reflog - 查看版本详细信息
git log - 版本穿梭
git reset --hard 版本号(版本号可以通过git reflog查询)通过HEAD^或HEAD~移动HEAD到相对位置
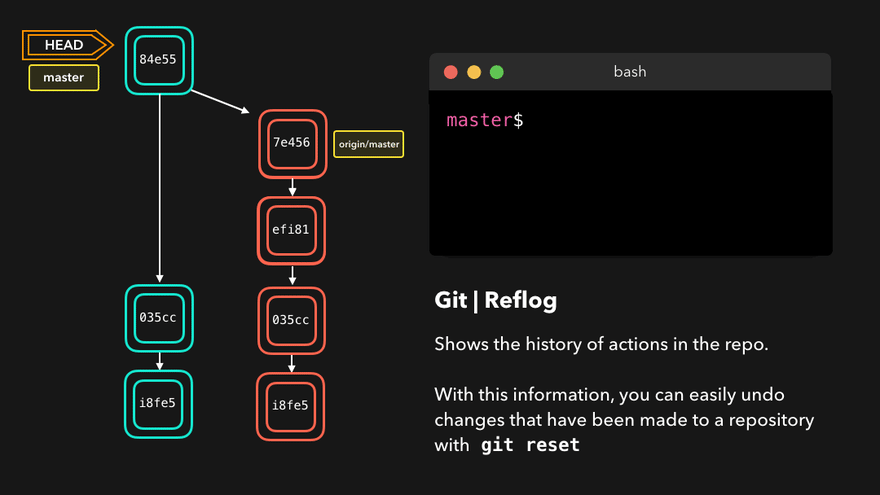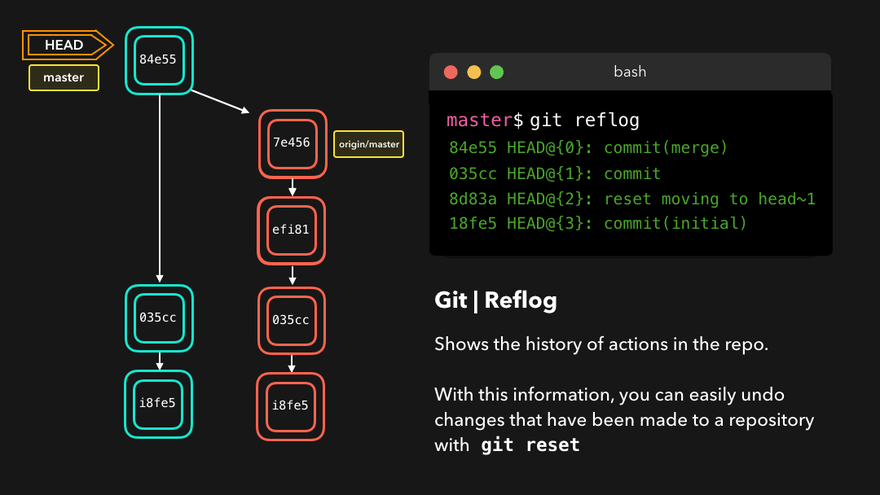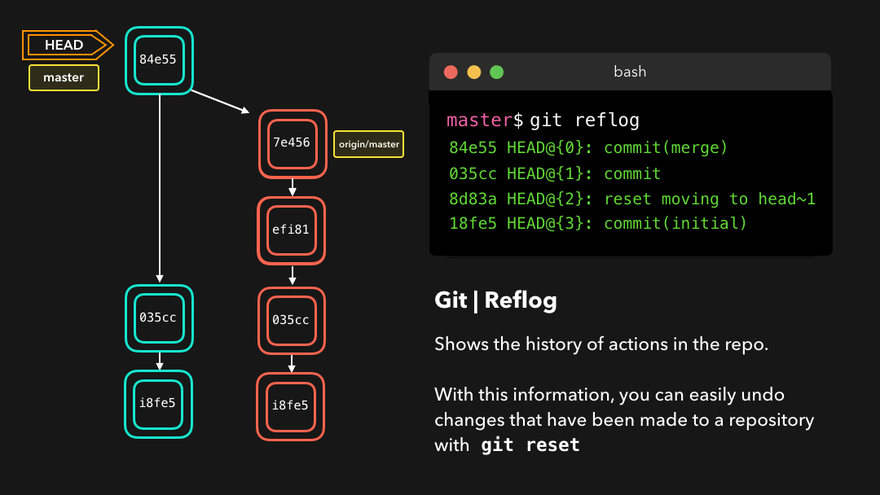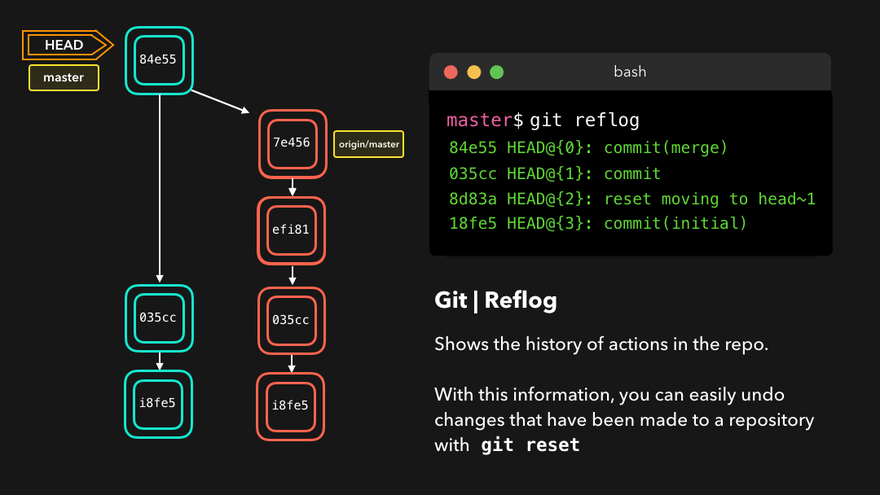
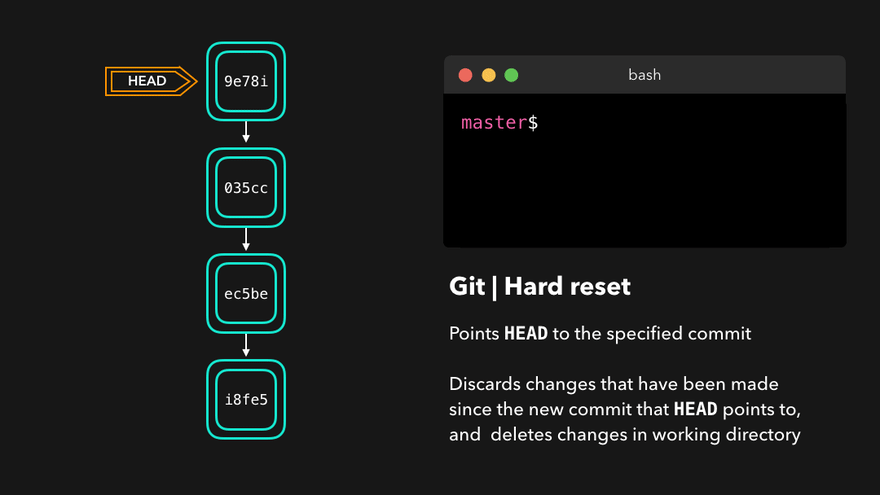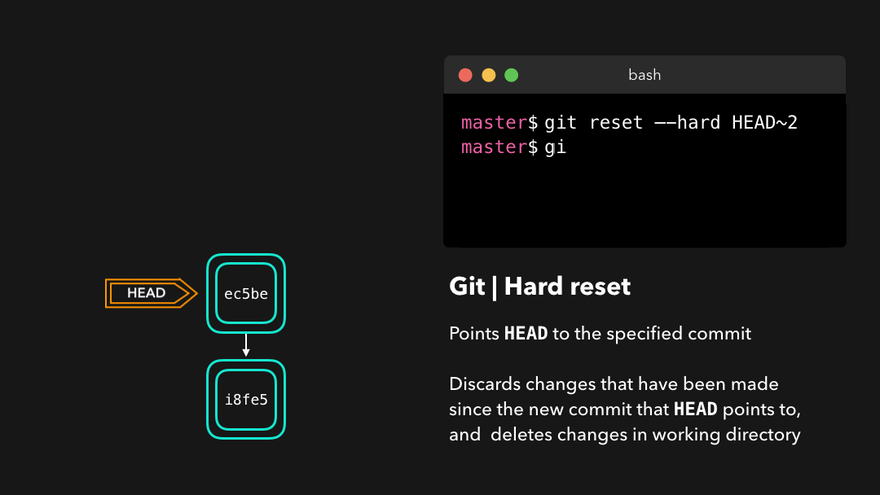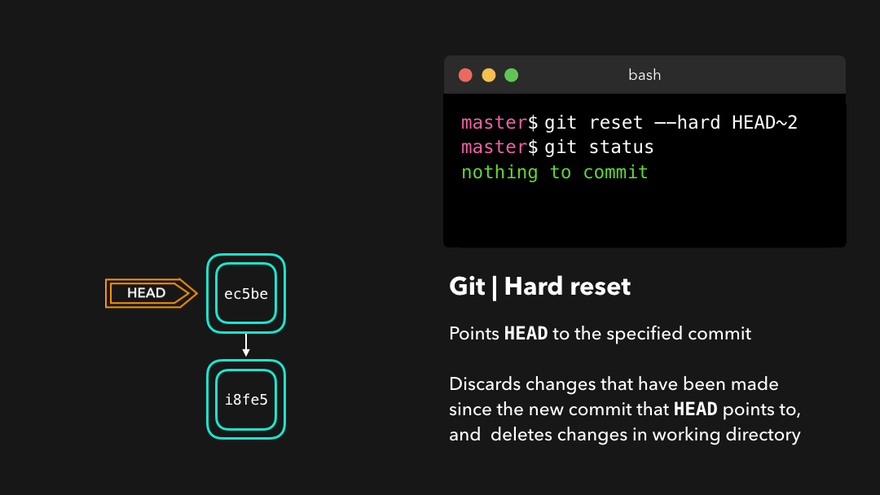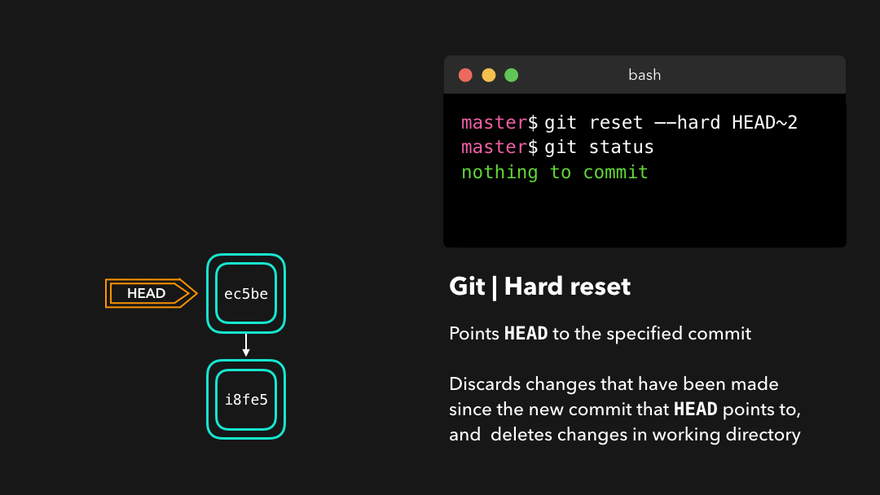
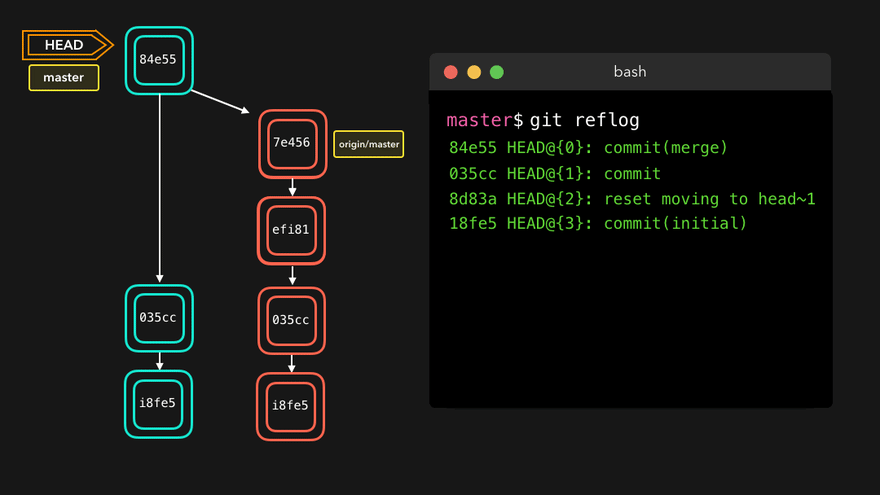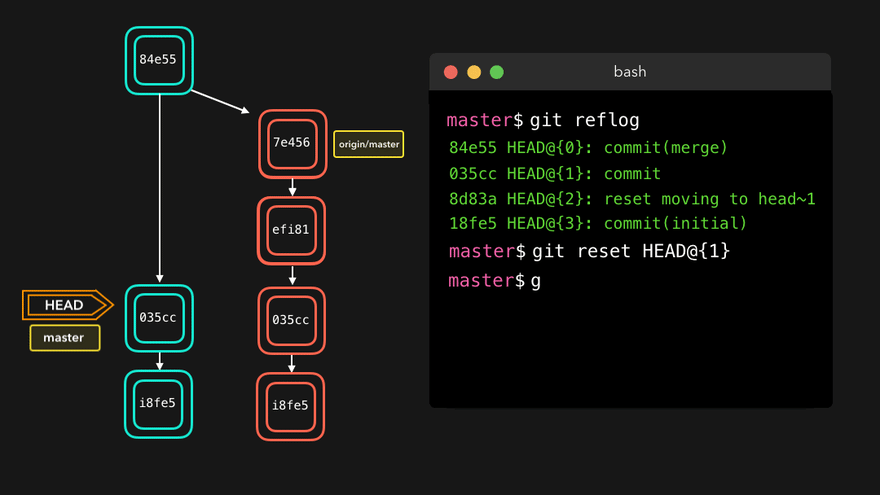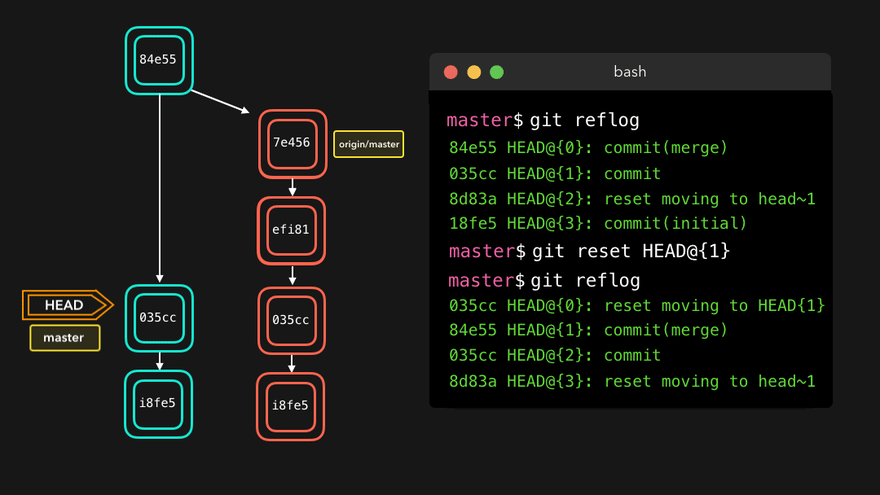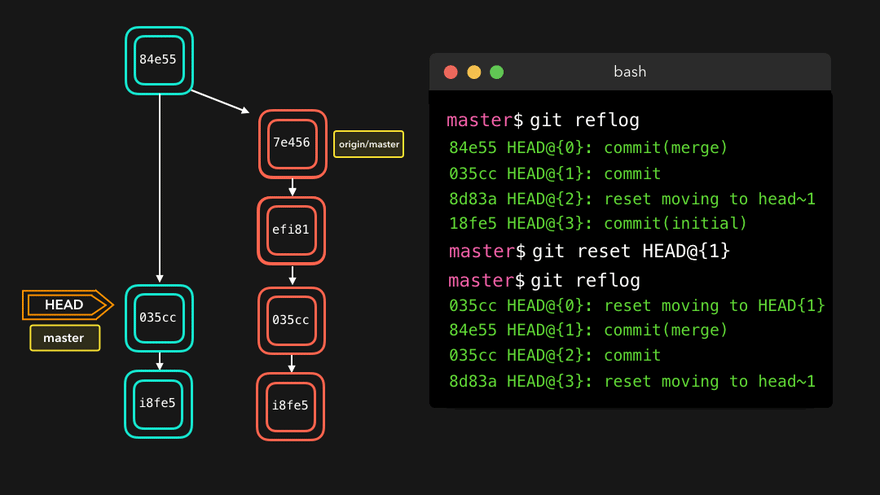
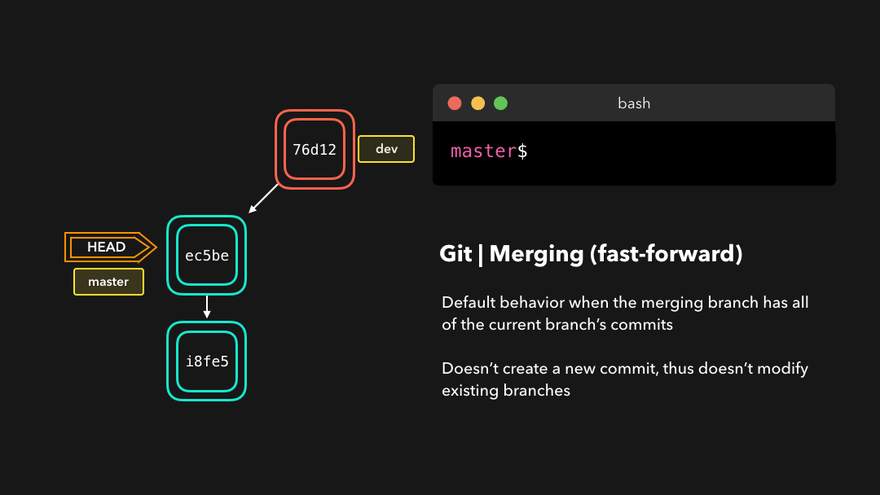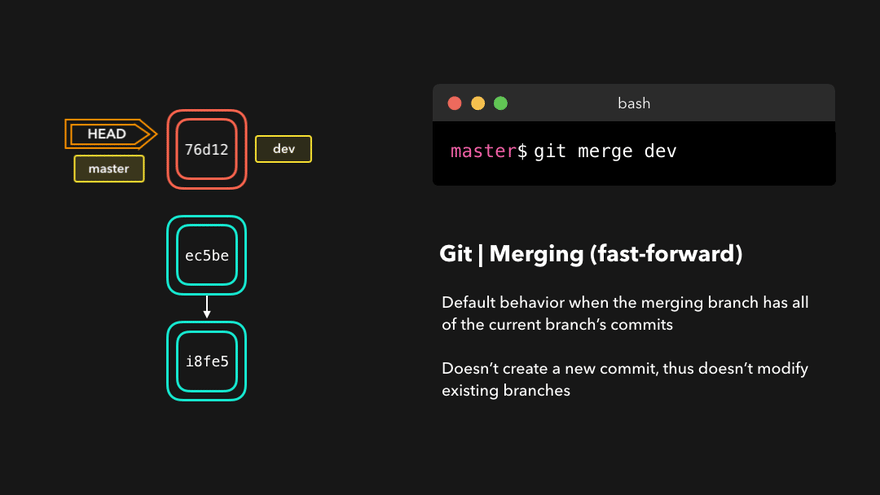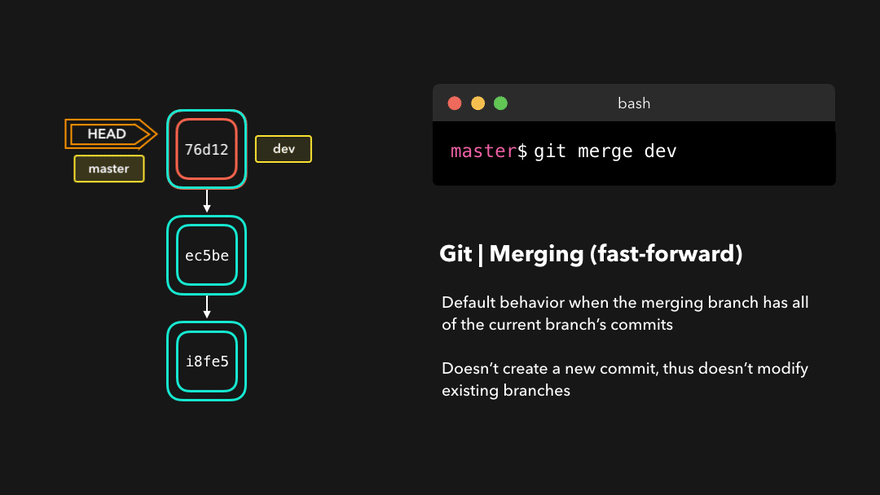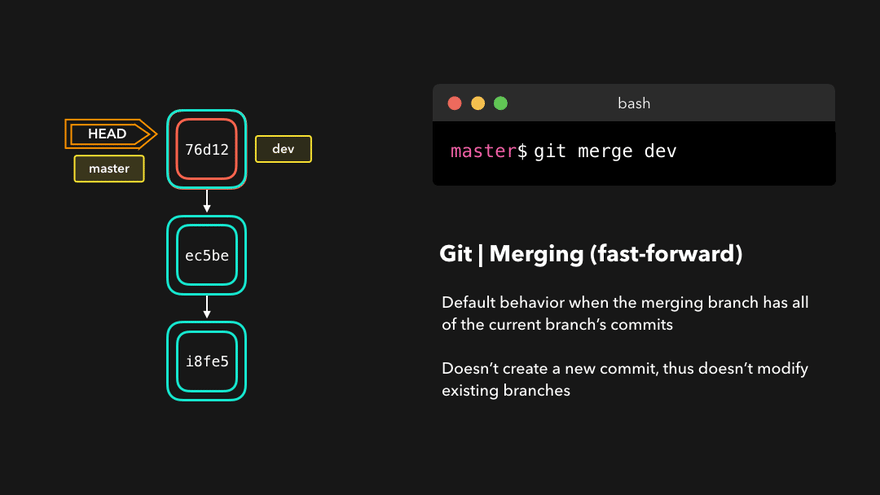
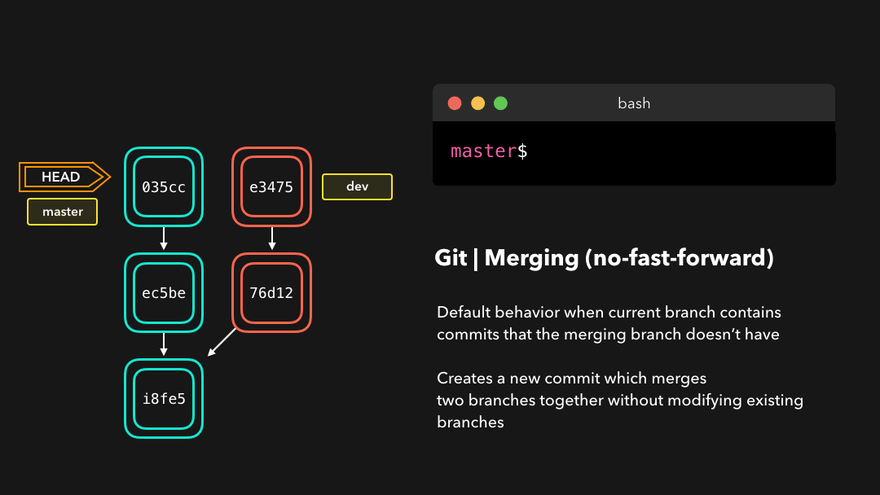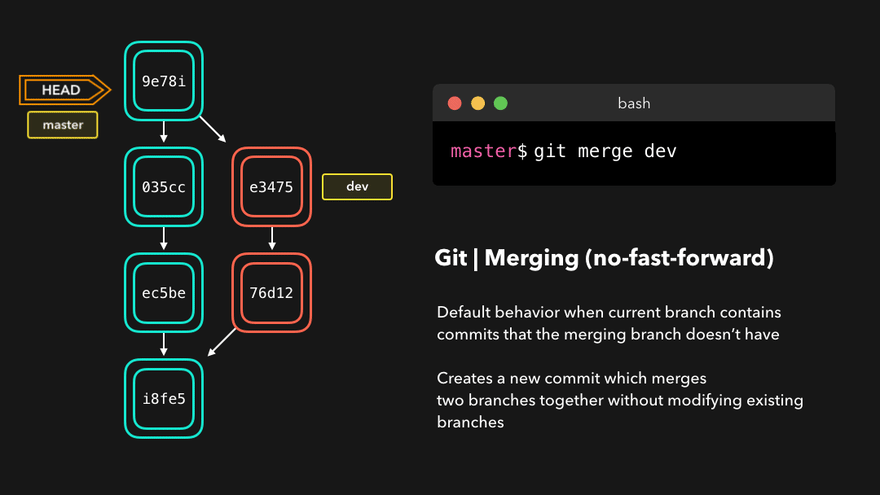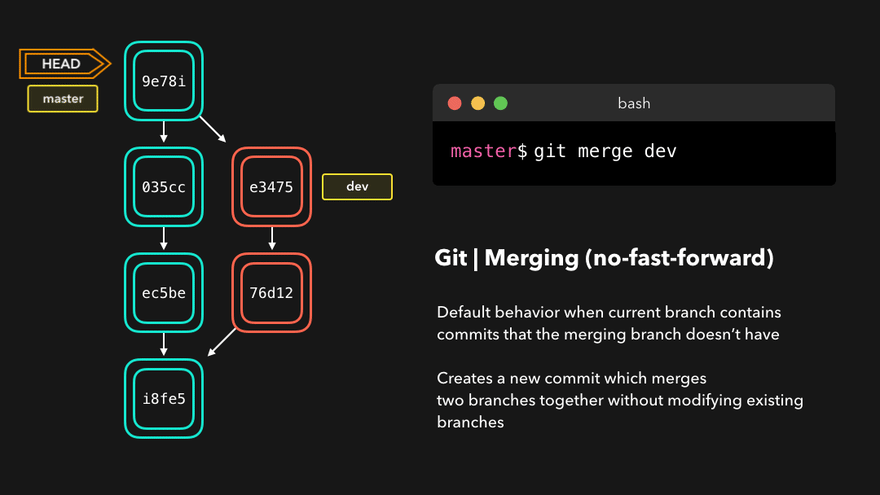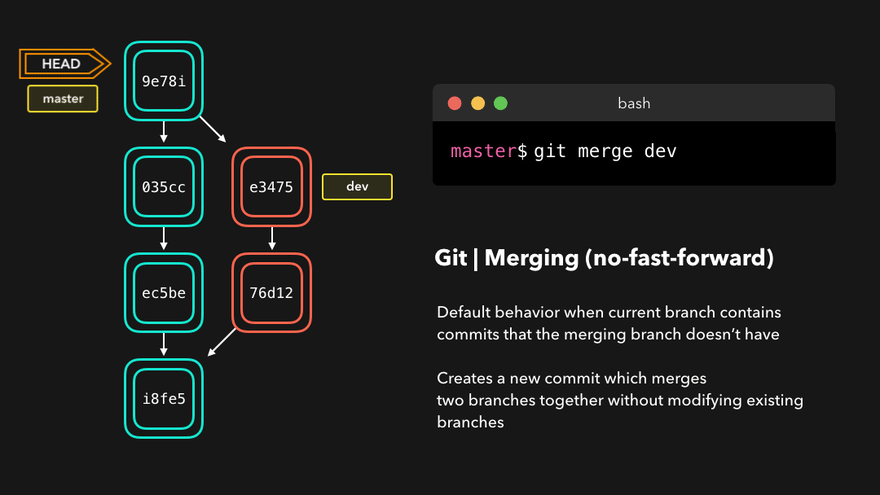
注意:上图中,链表结构从新版本指向旧版本,merge情况下指向两个父(旧)版本。
勘误:命令行结果中版本号应为i8fe5。左图中未显示8d83a版本号。
3. 分支操作
- 查看分支
git branch -v - 创建分支
git branch 分支名 - 切换分支
git checkout 分支名 - 合并分支
git merge 分支名(在master分支上,合并hot-fix分支) - 删除分支
git branch -d 分支名
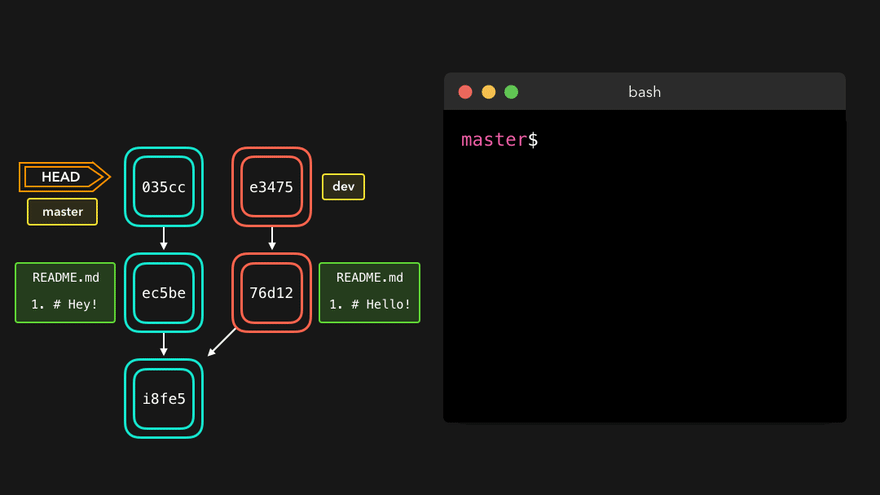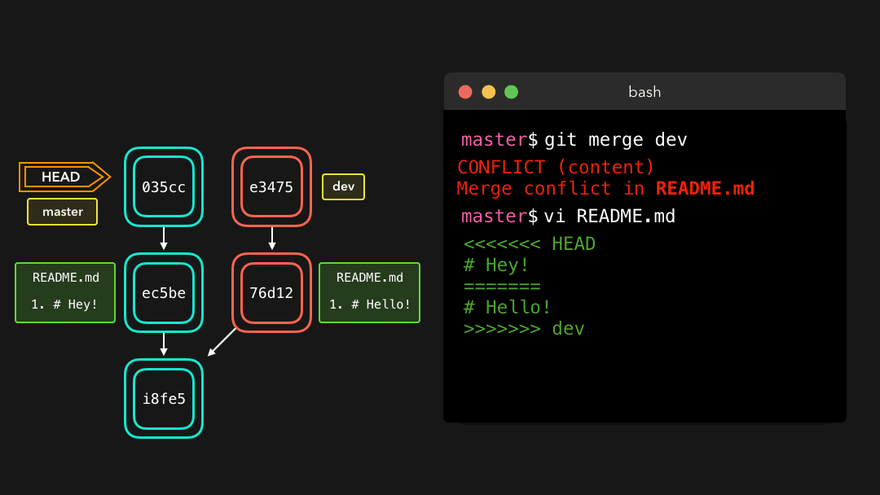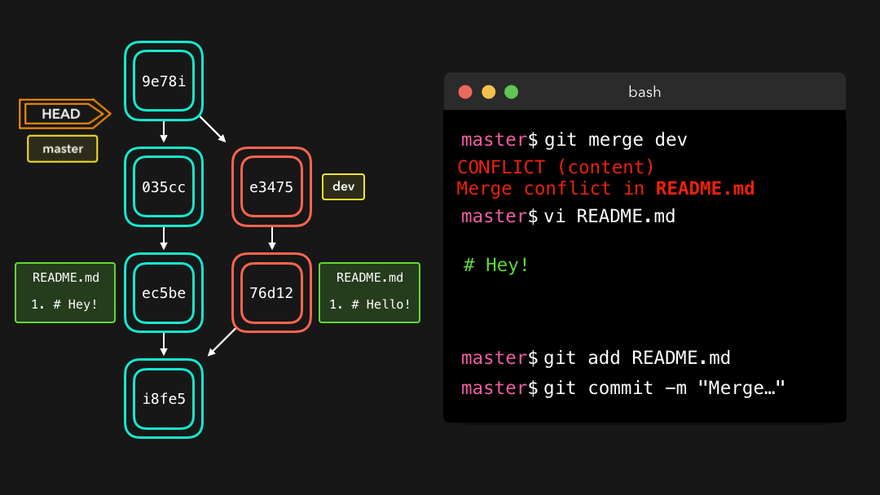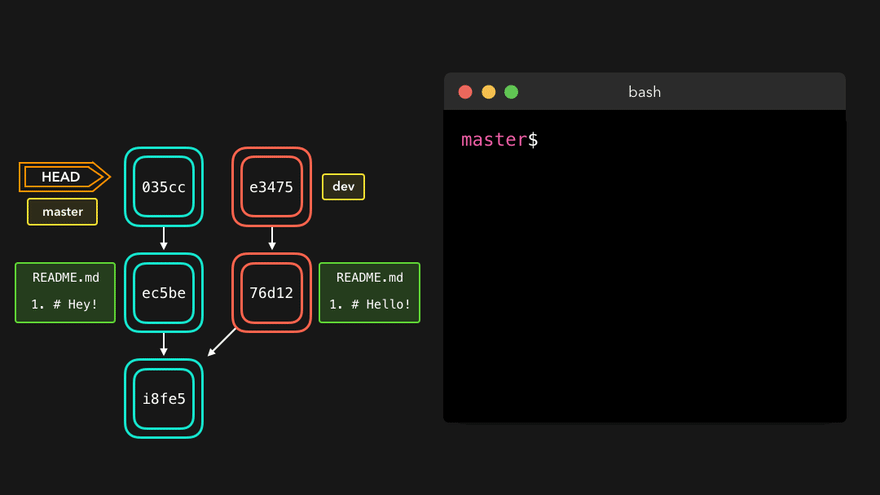
冲突产生的原因:合并分支时,两个分支在同一个文件的同一个位置有两套完全不同的修改。Git无法替我们决定使用哪一个。必须人为决定新代码内容。
冲突
<<<<<<< HEAD
abc (当前分支修改)
=======
def (并入分支修改)
>>>>>>> hot-fix
注意:人为决定采用哪种修改后,仍然需要git add与git commit使得合并过程从merging到merged状态。
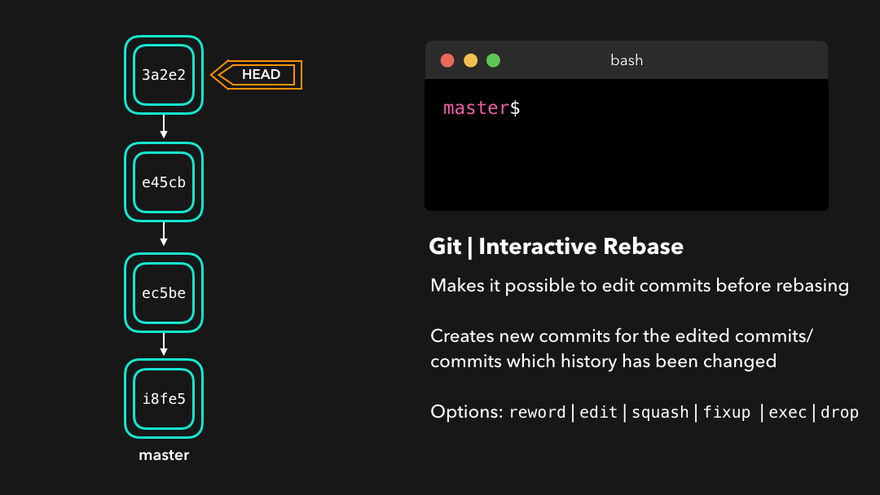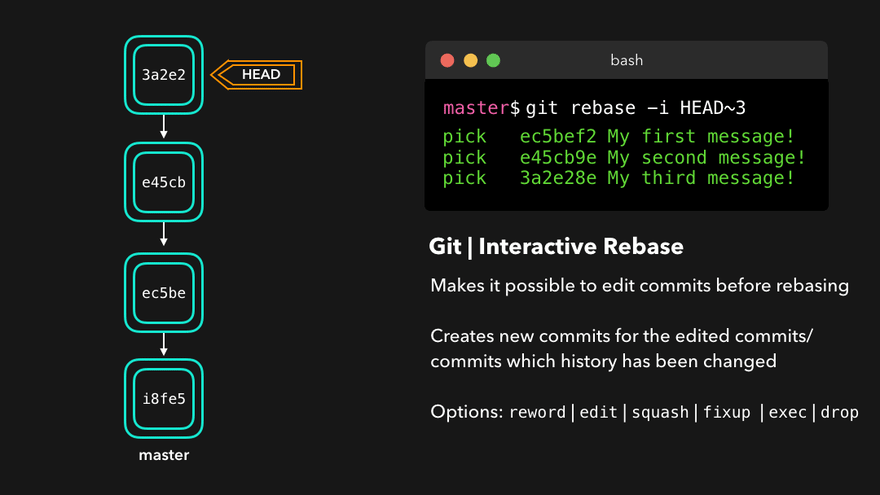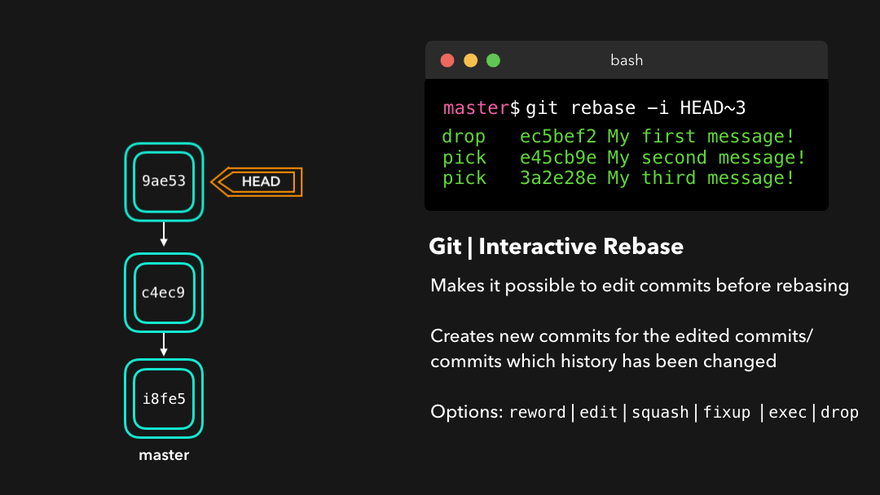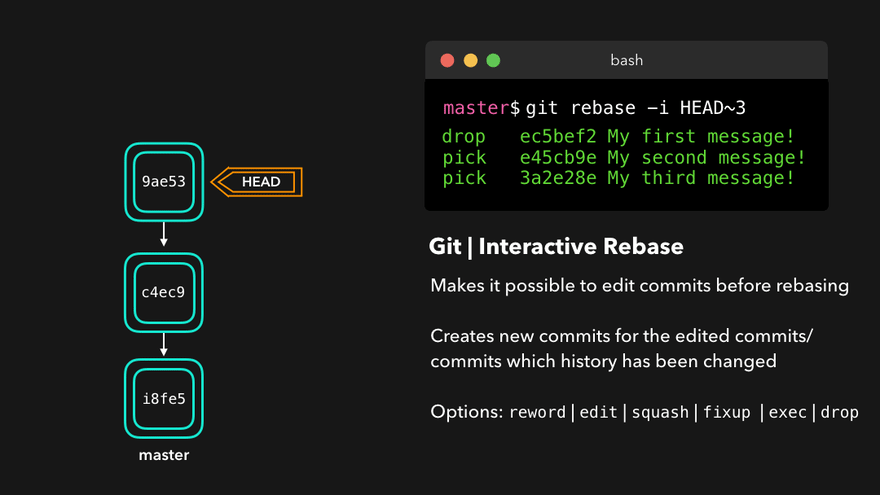
理解底层指针:Head指针指向分支名(如master),master指针指向版本号
4. 团队协作机制
- 查看本地保存到远程库地址
git remove -v - 给远程库起别名
git remove add 别名 远程地址例如git remote add origin https://github.com/username/reponame.git - 将本地当前分支推送到远程某分支
git push 远程库别名 远程库分支例如git push origin master - 将远程某分支拉取到本地当前分支
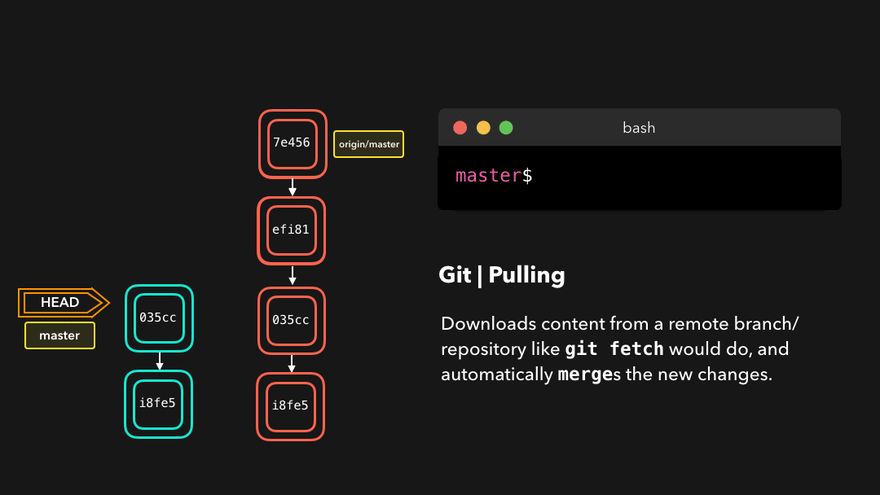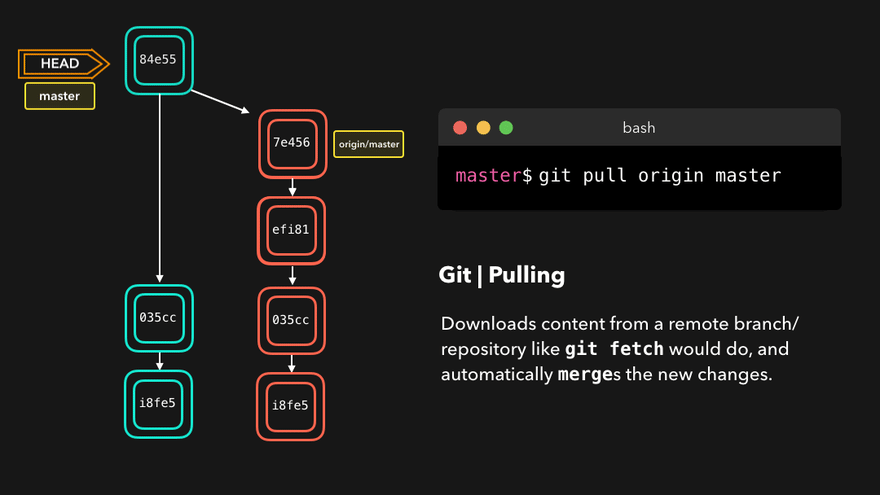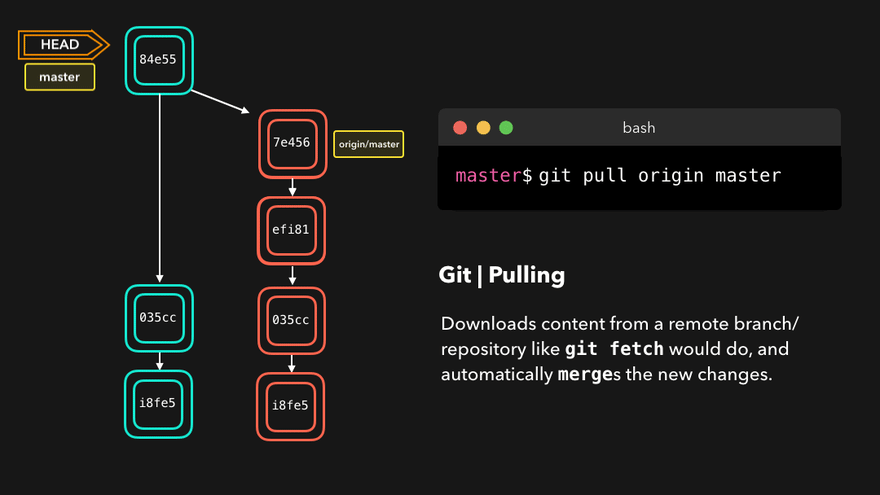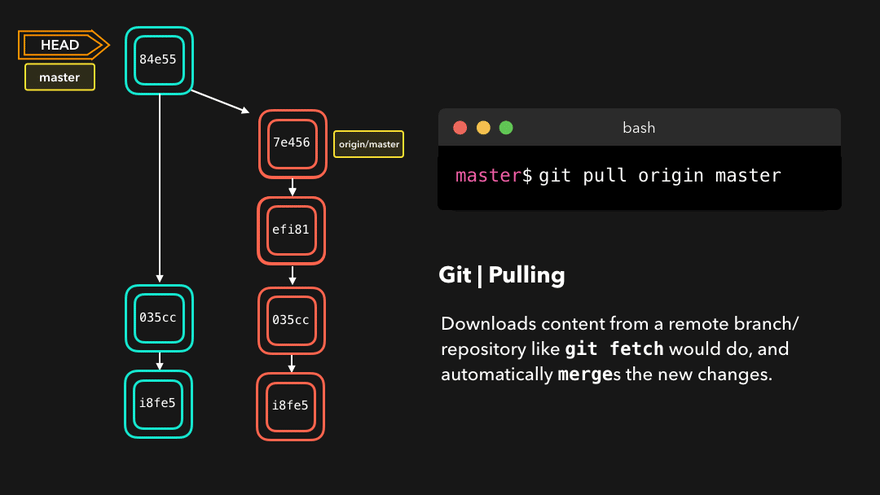
git pull 远程库别名 远程库分支例如git pull origin master - 取得远程库某分支
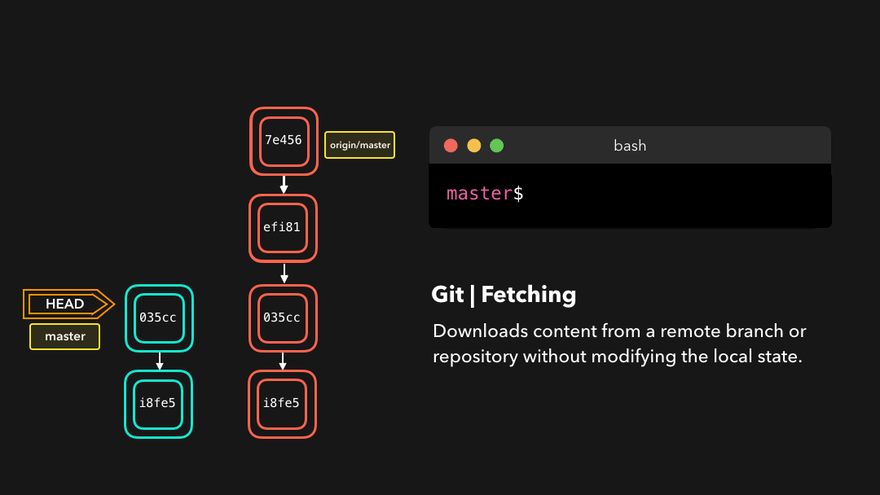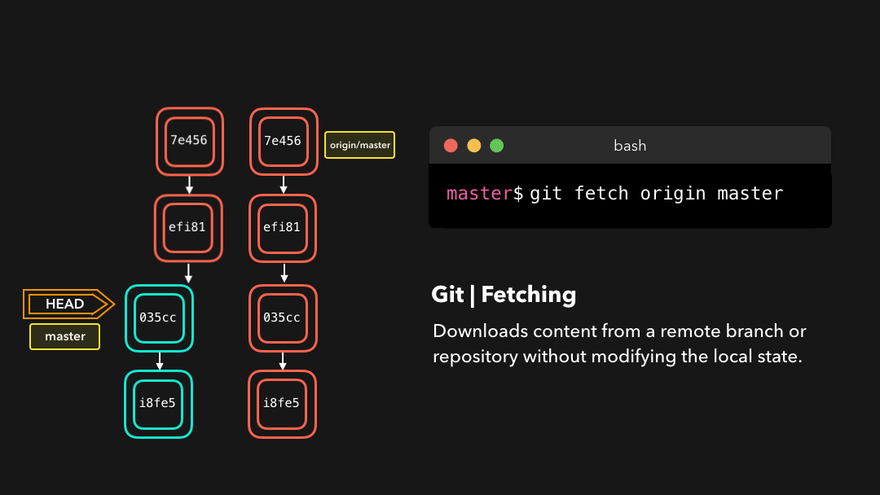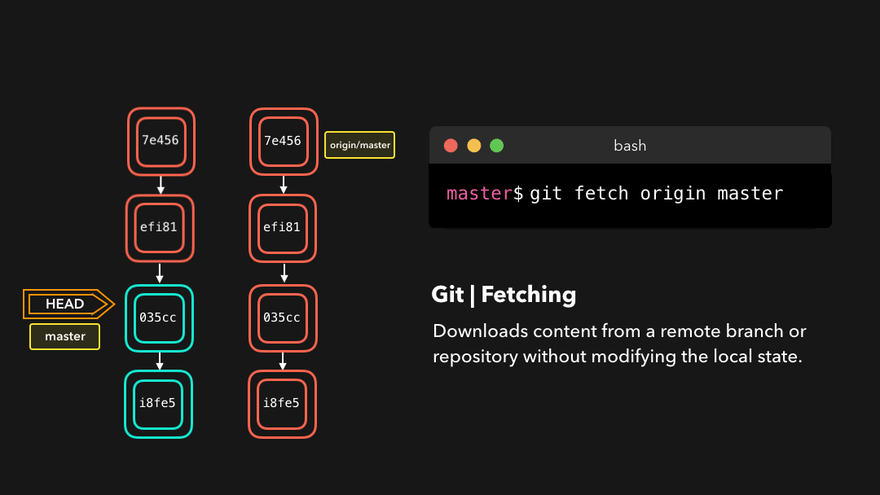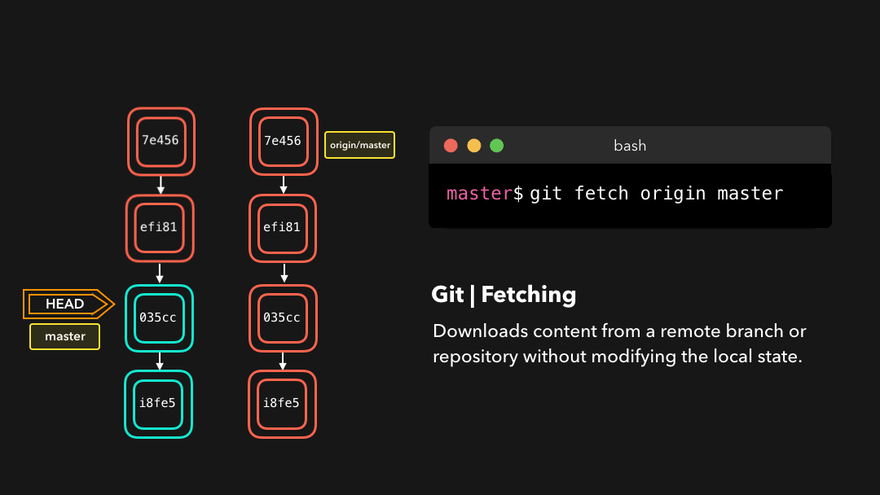
git fetch 远程库别名 远程库分支例如git fetch origin master - 克隆远程库到本地
git clone 远程库地址(clone会做三件事:1.拉取代码 2.初始化本地库 3. 创建别名)
注意:push是将本地库代码推送到远程库,如果本地库代码跟远程库代码版本不一致,push的操作是会被拒绝的。也就是说,要想push成功,一定要保证本地库的版本要比远程库的版本高!因此一个成熟的程序员在动手改本地代码之前,一定会先检查下远程库跟本地代码的区别!如果本地的代码版本已经落后,切记要先pull拉取一下远程库的代码,将本地代码更新到最新以后,然后再修改,提交,推送!
问题:What’s the main difference between git fetch and git pull? git fetch fetches remote updates but doesn’t merge; git pull fetches remote updates and merges.
git fetch origin master
git checkout origin/master
git merge origin/master
注意:“origin” is the default name for the remote repo.
5. 工作流
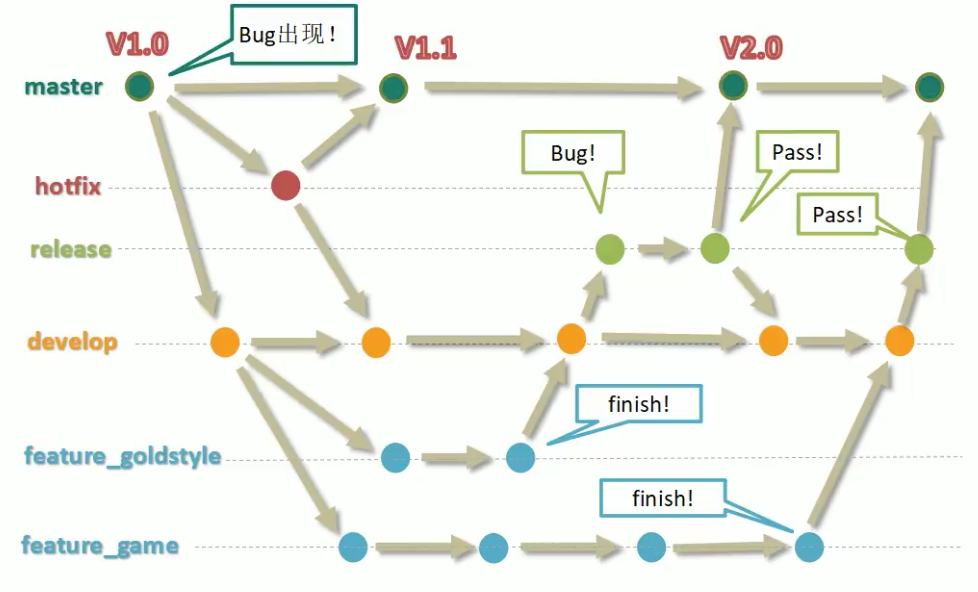
Steps:
- (junior)创建分支feature
- (junior)推送feature分支
- (senior)切换分支,审查代码
- (senior)切换master,合并feature
- (senior)推送master分支
TODO
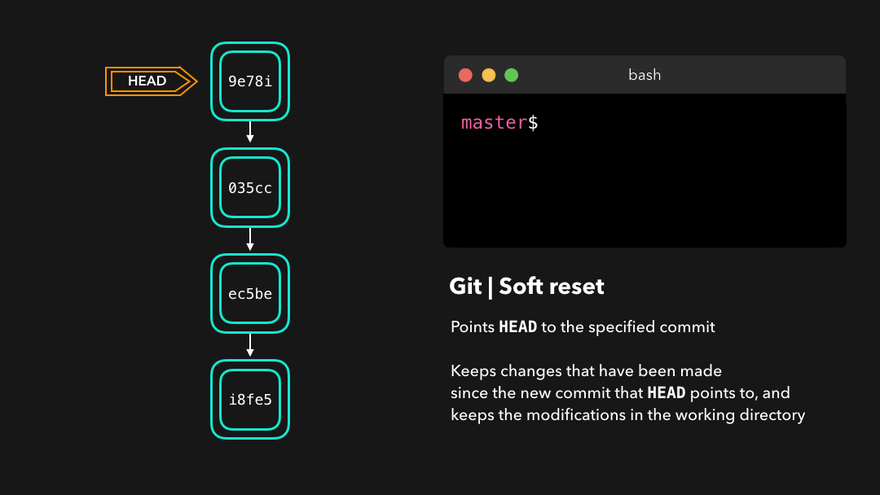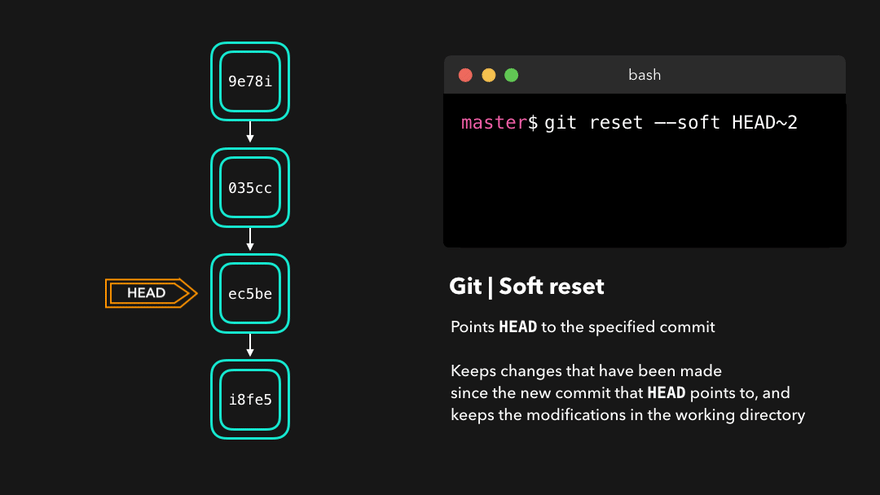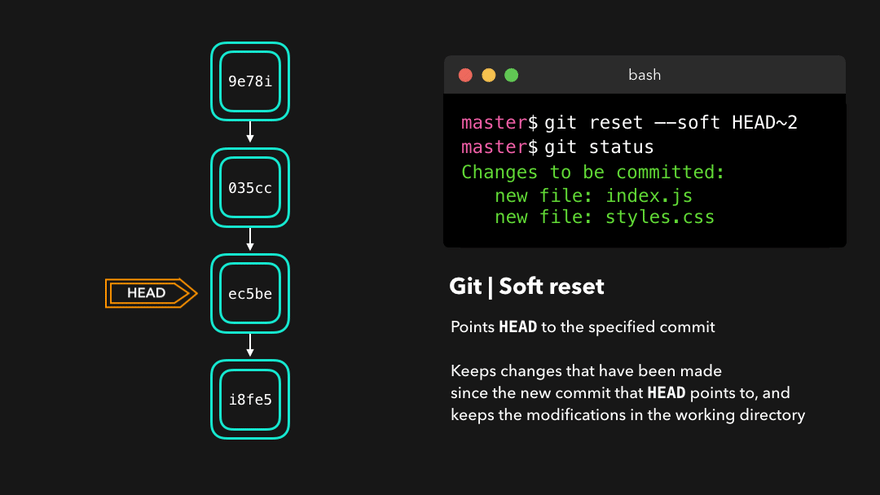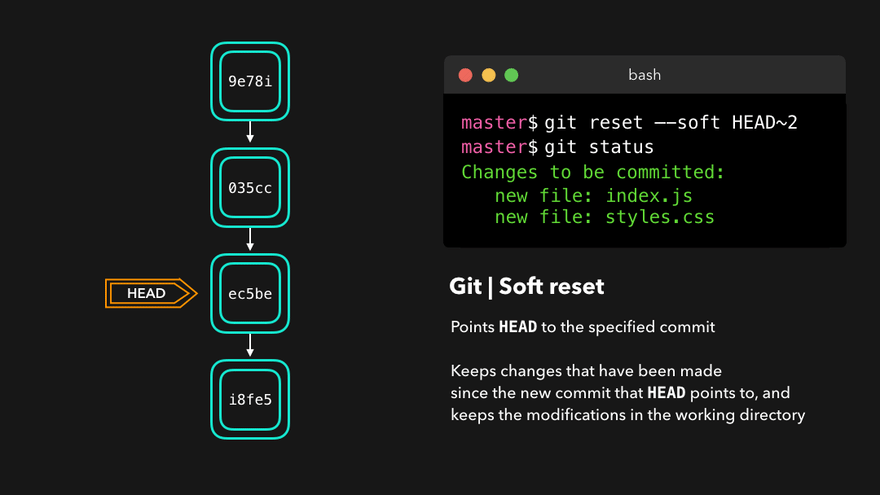
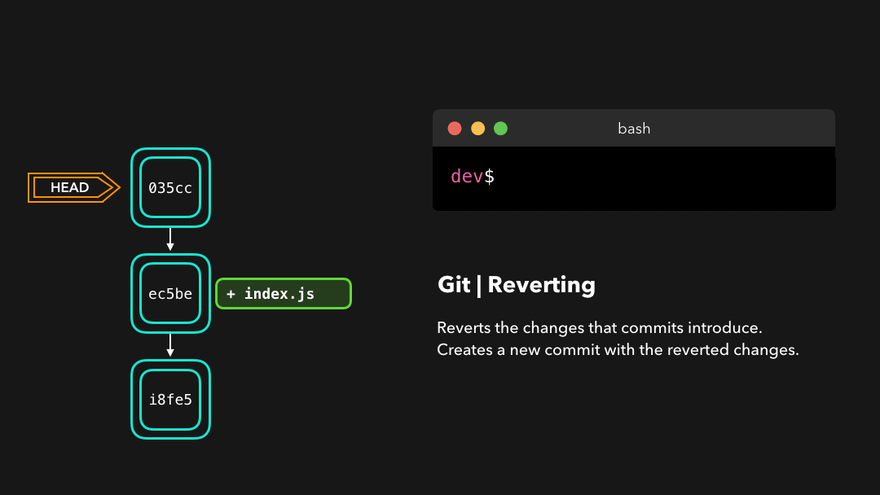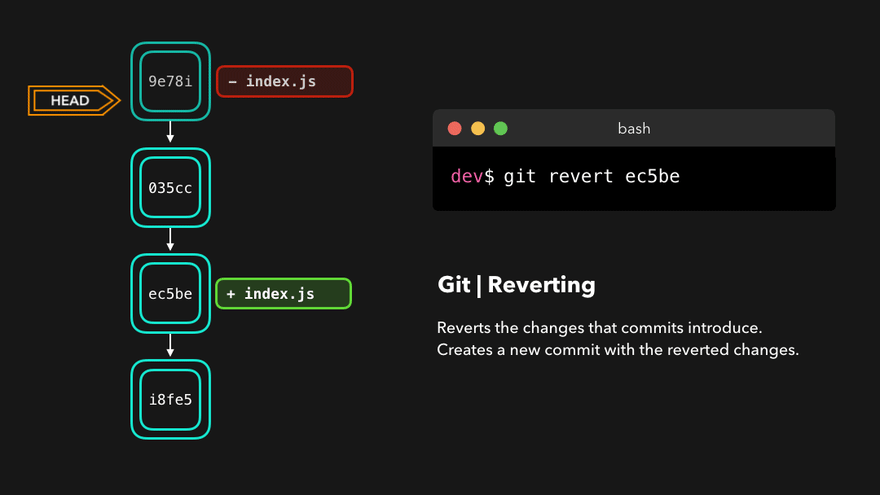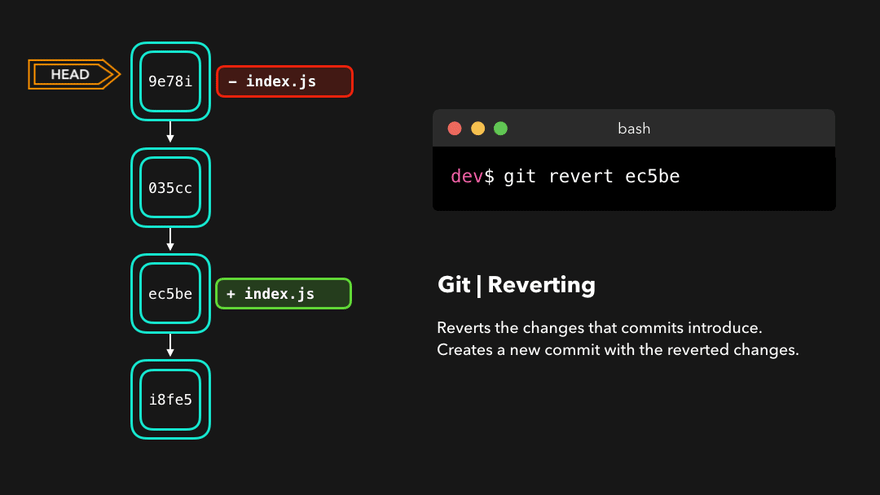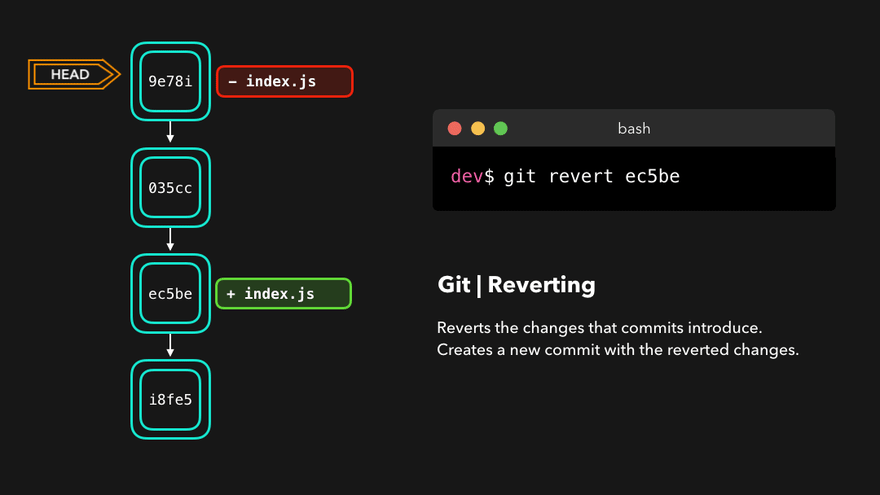
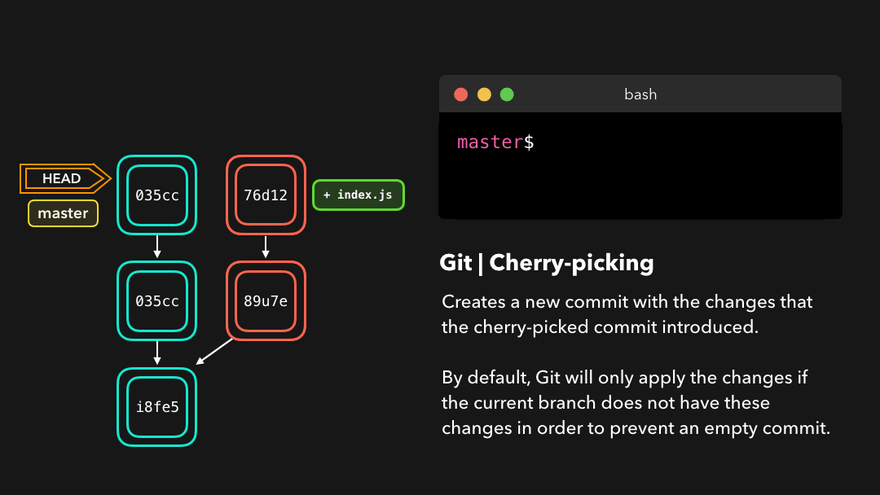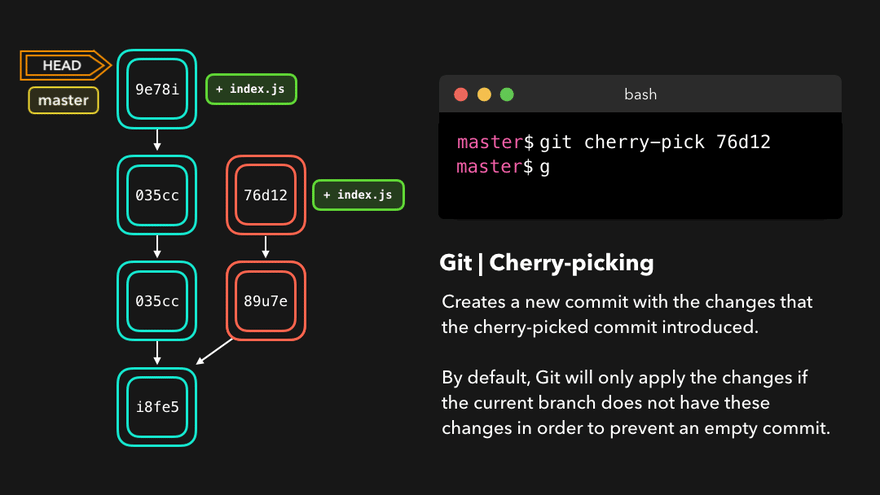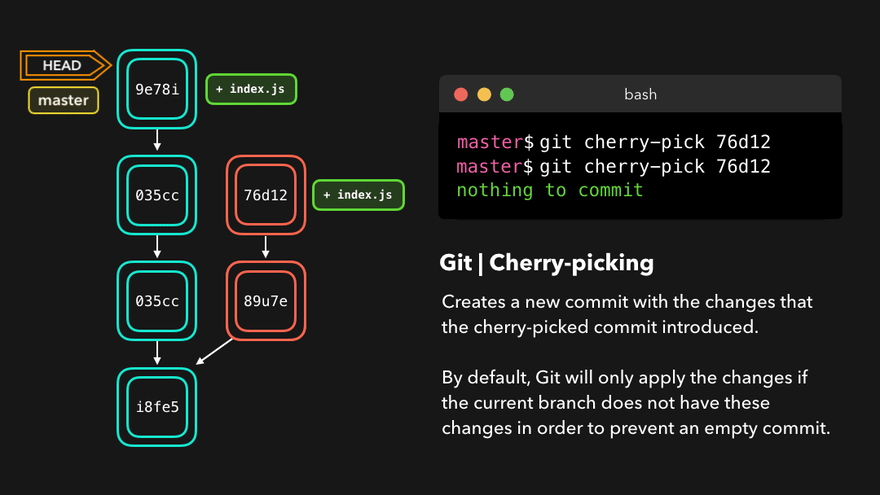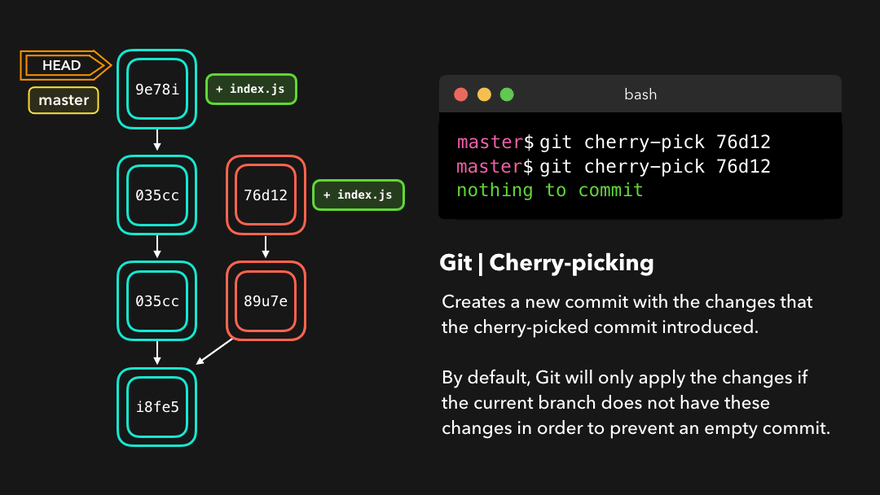
撤销
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
git remote update will update all of your branches set to track remote ones, but not merge any changes in.
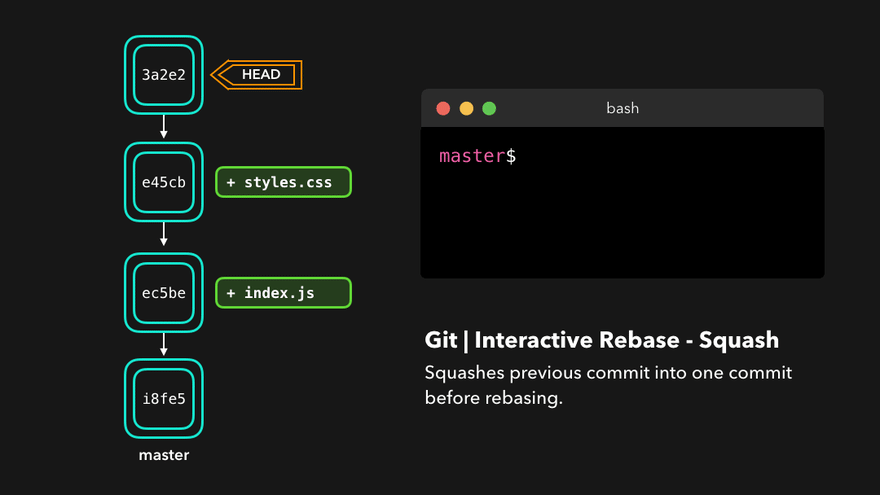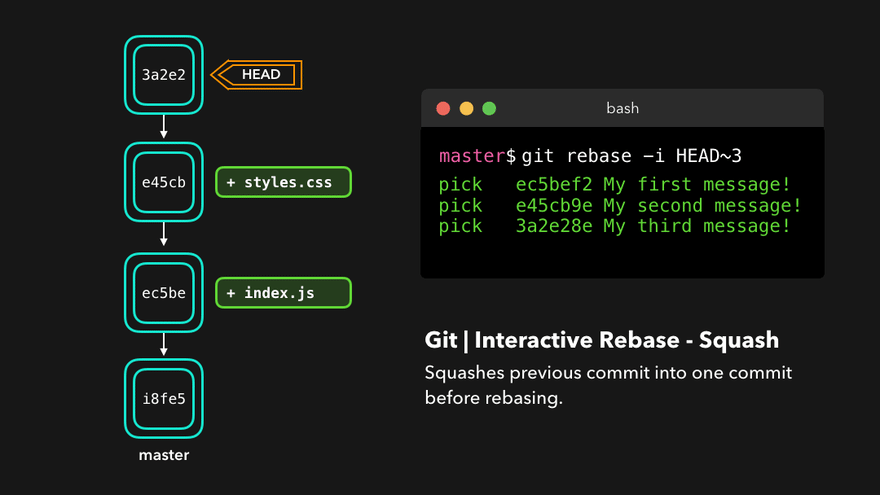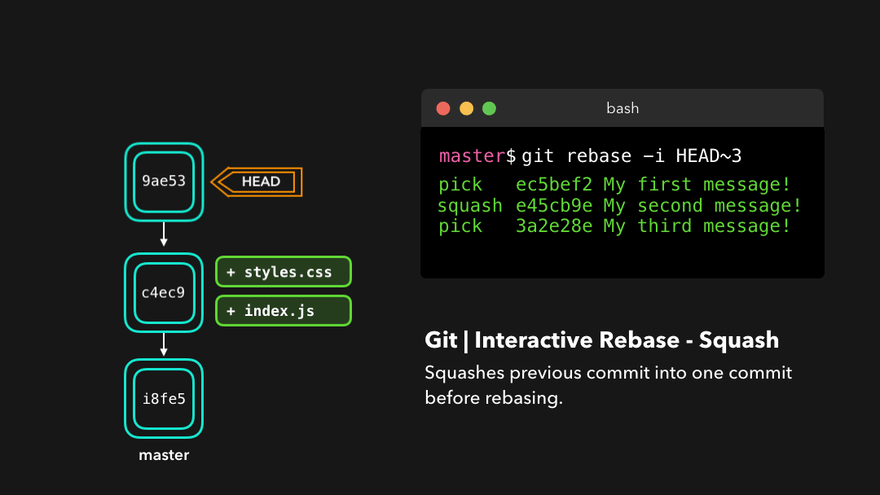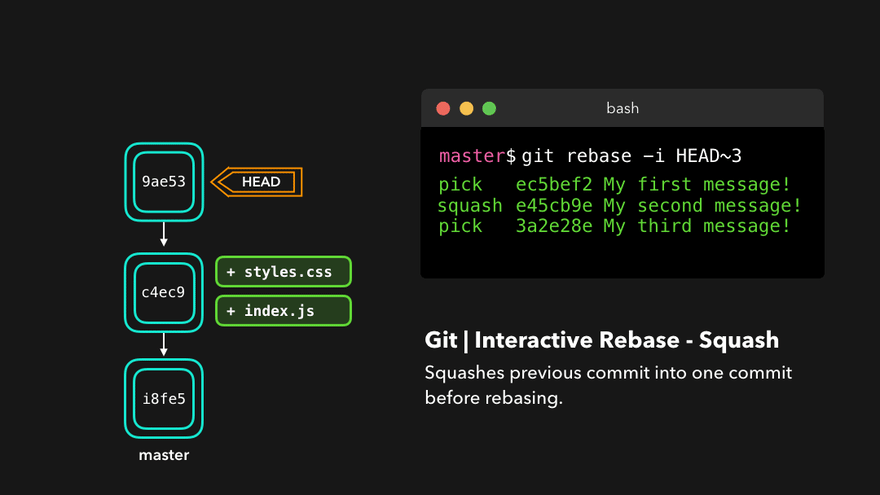
Rebasing instead of merging rewrites history and maintains linearity, making for cleaner code.
|
|
|
|
|
|
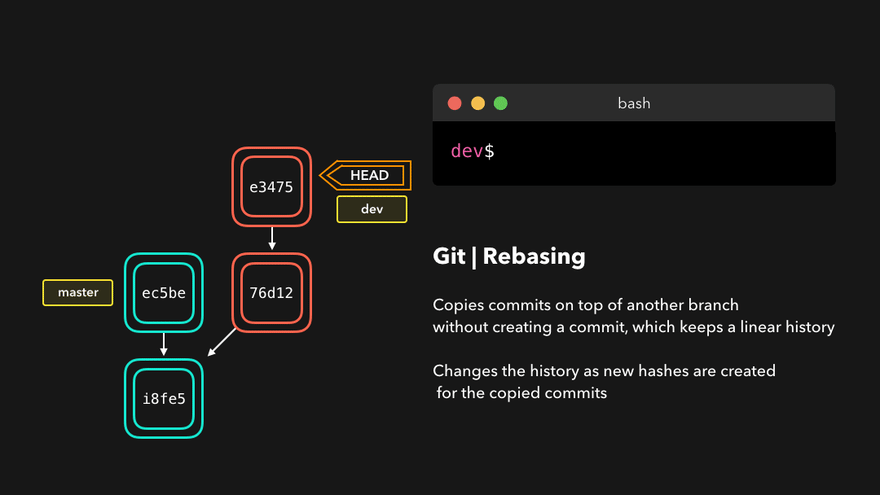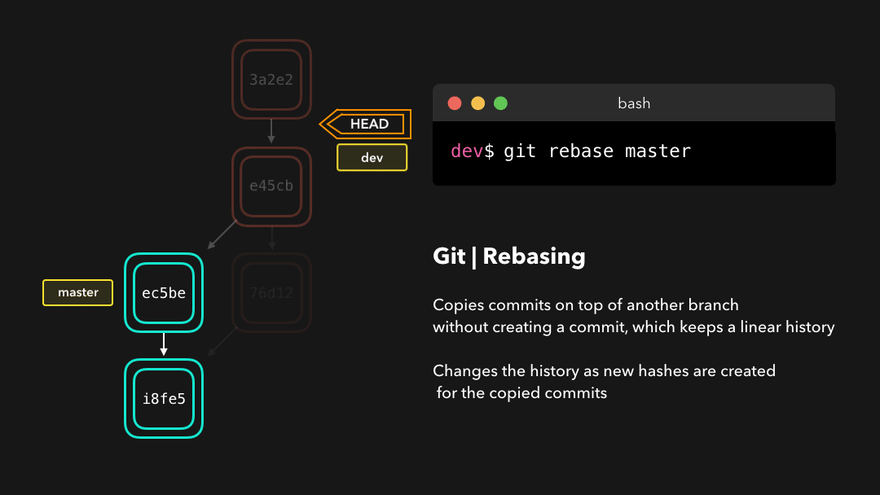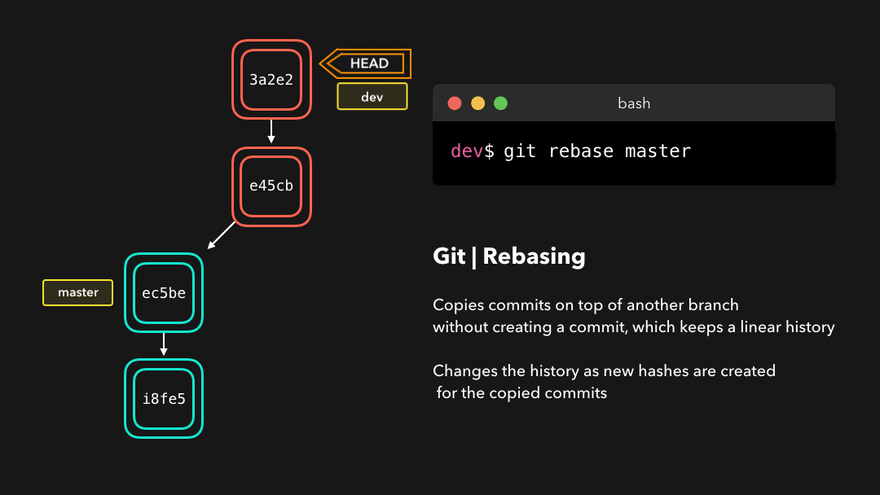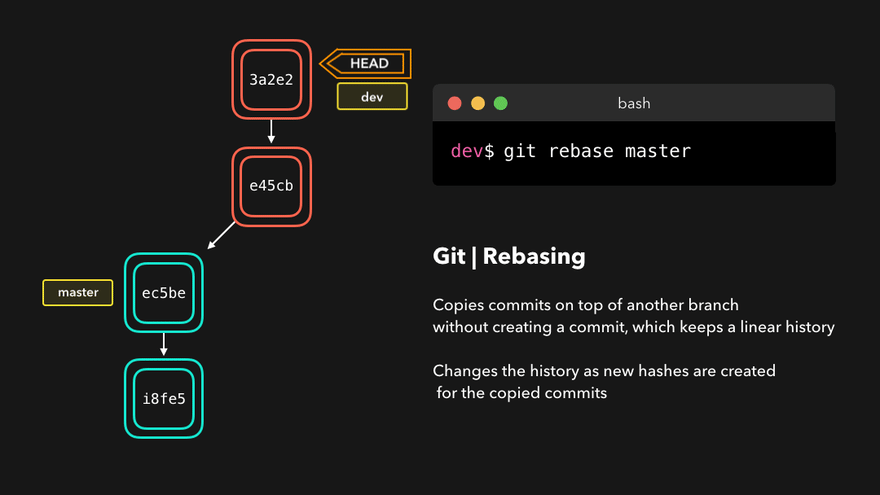
参考
CS Visualized: Useful Git Commands - Lydia Hallie
What is the difference between ‘git remote update’, ‘git fetch’ and ‘git pull’?
Listing and deleting Git commits that are under no branch (dangling?)
How can I undo git reset –hard HEAD~1?